In cooperation with Björn, it is splitted on "Disease is Different" into the sections by organ systems and combined with the real cases of our international testimonial / report archive of the related organ system.
BLADDER
The bladder (vesica urinaria) as a hollow organ composed of smooth muscle. (According to Dr. Hamer, striated). The bladder collects the urine produced in the kidneys via both ureter and stores it until it is emptied over the urethra. The greater part of the bladder is lined with ectodermal tissue, so-called urothelium (transitional cells). Below it lies the endodermal bladder mucousa. The one exception: in the “bladder triangle“ (Trigonum vesicae), a small island of endodermal mucosa protrudes from beneath the urothelium.
The bladder has two sphincter muscles at its transition to the urethra: the inner one (M. sphincter urethrae) is smooth and involuntary and the outer one (M. sphincter vesicae) is striated and voluntary.
The discharge of urine is proceeds in the form of a repair phase crisis of the bladder muscles. (The repair phase crisis as a functional building block of nature.)
Deep-Lying Bladder Mucosa, Trigone
Hardly digestible,
ugly situation
Superficial Bladder Mucosa
Territory-marking conflict
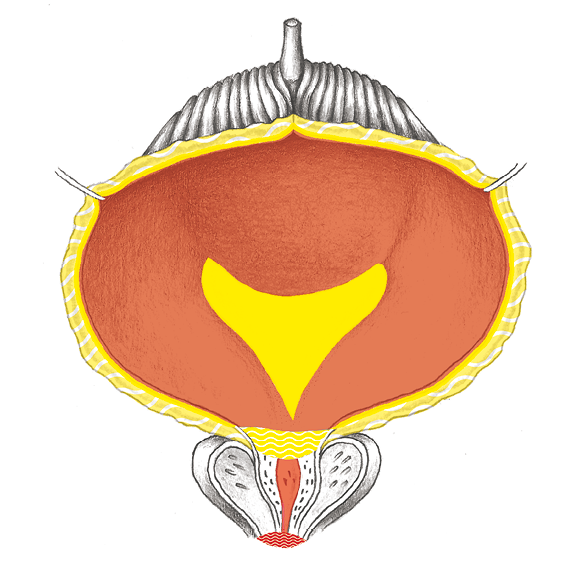
External Urethral Sphincter
Not being able to
hold back the urine
Internal Urethral Sphincter
Not being able to hold back the urine/chunk
Bladder Musculature
Can‘t expel the urine
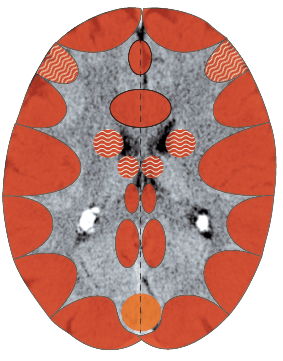
Inflammation of the bladder (urocystitis), cancer of the
transitional epithelium of the bladder (urothelium cancer,
urothelium papilloma, inverted papilloma)1
| Conflict | Territory marking conflict; the borders of the territory are not respected, one is not able to mark the borders of the territory. Conflict explained under renal pelvis SBS, p. 282 (with more examples). |
|---|---|
| Examples |  A patient can perfectly remember one of the most horrible experiences of her youth: She is 13 years old and her father, whom she describes as a “tyrant and sadist,“ deliberately kills her beloved rabbit for no reason. She wanted to “go crazy.“ Her father also overstepped her boundaries in other situations as well. She cannot defend her boundaries or mark them = territory-marking conflict. In the repair phase , she contracts an inflammation of the bladder. Since then, whenever she is nervous, she suffers from an urgent need to empty her bladder (= irritable bladder). (Archive B. Eybl) A patient can perfectly remember one of the most horrible experiences of her youth: She is 13 years old and her father, whom she describes as a “tyrant and sadist,“ deliberately kills her beloved rabbit for no reason. She wanted to “go crazy.“ Her father also overstepped her boundaries in other situations as well. She cannot defend her boundaries or mark them = territory-marking conflict. In the repair phase , she contracts an inflammation of the bladder. Since then, whenever she is nervous, she suffers from an urgent need to empty her bladder (= irritable bladder). (Archive B. Eybl) One evening, the mother storms into her daughter‘s bedroom because she is “endlessly“ talking on the telephone. The daughter cannot believe that her mother shamelessly barged into her “space“ > cell degradation in the mucosa of the bladder, restoration in the repair phase. She repeatedly gets a “bladder infection“ (= repair phase) when her mother interferes in her life = trigger. (See www.germanische-heilkunde.at/index.php/erfahrungsberichte). One evening, the mother storms into her daughter‘s bedroom because she is “endlessly“ talking on the telephone. The daughter cannot believe that her mother shamelessly barged into her “space“ > cell degradation in the mucosa of the bladder, restoration in the repair phase. She repeatedly gets a “bladder infection“ (= repair phase) when her mother interferes in her life = trigger. (See www.germanische-heilkunde.at/index.php/erfahrungsberichte).  For three years now, an 18-year-old has had a recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI), despite antibiotics, with blood in her urine and nighttime cramps. Her mother had the same complaints up until three years ago. Then it started with her (= indication of a family conflict). It started when she began dating her first boyfriend. She was 15, he was 28 – dominant over her in all respects. She was afraid it might not work because of their age difference = territorial-marking conflict. For three years now, an 18-year-old has had a recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI), despite antibiotics, with blood in her urine and nighttime cramps. Her mother had the same complaints up until three years ago. Then it started with her (= indication of a family conflict). It started when she began dating her first boyfriend. She was 15, he was 28 – dominant over her in all respects. She was afraid it might not work because of their age difference = territorial-marking conflict. Her second boyfriend was 16, on the weak side, and she knew he wouldn’t leave her. > Now, she hardly experienced any more bladder infections = resolution. Her third boyfriend was a great guy, a little older, but suitable. He cheated on her once, so she was often jealous. After that, she went back to having persistent infections again = renewed territorial-marking conflict. In speaking with her, it became clear that she has not been able to cope with her parents’ divorce. Therapy: In a meditation, I told her on behalf of her father, “Maria, I was always incredibly proud of you. That your mother and I got a divorce has nothing to do with you.” She began taking transdermal magnesium for the nighttime cramps. After the first treatment, she has been symptom-free for four weeks. For “homework” she uses the following affirmation: People come, and people go – that is completely okay. (Archive B. Eybl)  Bladder-Urethra-Ca: A 76-year-old farmer handed over his business to his son two years ago in the hope that their ailing relationship would improve. However, it actually got worse – His son didn’t want to be told anything anymore. So, the patient and his wife were still running the company = territory-marking conflict. In our conversation, it became clear that the patient was following in the footsteps of his mother: possessive, not wanting to give anything away. The therapy was clear: He should hand over the business completely, give his son his blessing and leave him alone. An operation was unavoidable due to the size of the tumor. (Archive B. Eybl) Bladder-Urethra-Ca: A 76-year-old farmer handed over his business to his son two years ago in the hope that their ailing relationship would improve. However, it actually got worse – His son didn’t want to be told anything anymore. So, the patient and his wife were still running the company = territory-marking conflict. In our conversation, it became clear that the patient was following in the footsteps of his mother: possessive, not wanting to give anything away. The therapy was clear: He should hand over the business completely, give his son his blessing and leave him alone. An operation was unavoidable due to the size of the tumor. (Archive B. Eybl)➜ Term “honeymoon cystitis“ (cystitis during their honeymoon). Conflict resolution of a female territorial-marking conflict by the exhilaration from their time together. |
| Conflict-active | Decrease in sensibility of the bladder‘s mucosa, the ureter or urethra. Simultaneous slackening of the bladder’s ring and/or sphincter muscles respectively. Later, cell degradation (ulcer). No pain, no bleeding. The need to distance oneself; one pays strict attention to the territorial boundaries, is irritated, hypersensitive. |
| Bio. function | With relaxed ring and/or sphincter muscles, the territory can be marked extensively. |
| Repair phase | Restoration of the mucosa = inflammation of the bladder, ureter, or urethra = bladder ca (urothelium ca), swelling of the mucous membrane, pain, burning sensation by urination, frequent urge to urinate (pollakiuria), possibly blood in the urine (hematuria) and occasional loss of urine. Due to the healing-swelling, the flow can be blocked, especially with syndrome > urinary retention, incomplete emptying of the bladder. |
| Repair crisis | Pain, blood in the urine, bladder cramps caused by the involvement of the bladder muscles; possibly chills, absence seizures. |
| Note | 90% of bladder tumors are urothelium ca. Chronic bladder infection, recurring-conflict > scarred thickening of the mucosa (urothelium metaplasia) > “irritable bladder.“ |
| Therapy | Questions: see SBS of the renal pelvis p. 283. In the case of an individual bladder infection: The conflict is resolved. Support the repair phase. If recurring, identify the conflict, trigger(s), conditioning and resolve them. Guiding principles (if recurring): “I know what I want.“ “My space is my space.“ “I define the borders and they will be respected.“ For bladder remedies, see: p.292. |
Bed wetting (Enuresis nocturna)
Same SBS as above.
| Conflict | Territory-marking conflict: No space of one’s own (room). Neglect of the child’s needs. May indicate sexual abuse in extreme cases. Sometimes also the opposite situation: the territorial borders are lacking (anti-authoritarian upbringing). Since the child doesn’t have any territory, they mark the only territory available – their bed. |
|---|---|
| Examples | ➜ Birth of a sibling (perceived neglect). ➜ Divorce of the parents, moving house. ➜ No room of their own. |
| Phase | Repair phase crisis: Participation of the bladder musculature. |
| Questions | Is the child reflecting something for the parents? Mother/father under pressure? (Fighting in the relationship, divorce, overwhelming work environments, financial pressure)? Does the child have their own space? (Room, preschool)? Conflict/jealousy due to siblings? Do they long for attention? |
| Therapy | Determine and resolve the conflict, trigger(s) and conditioning. For bladder remedies, see: p.292. |
1 See Dr. Hamer, Charts pp. 117, 130
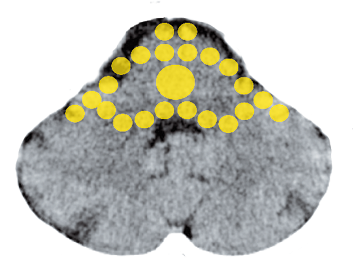
Purulent bladder infection, bladder cancer (adeno-ca)1
| Conflict | Hardly digestible, ugly situation. |
|---|---|
| Examples |  A 45-year-old human resources manager of a company is informed, in front of her whole team, that from now on, she will be an assistant in the HR office and her office, which was “her living room,“ will be given to the new manager. Years later, the patient is still talking about this outrage. Shortly afterwards, she is diagnosed with bladder cancer, which is then abraded. However, it keeps coming back because she cannot overcome what happened. (Archive of Antje Scherret) A 45-year-old human resources manager of a company is informed, in front of her whole team, that from now on, she will be an assistant in the HR office and her office, which was “her living room,“ will be given to the new manager. Years later, the patient is still talking about this outrage. Shortly afterwards, she is diagnosed with bladder cancer, which is then abraded. However, it keeps coming back because she cannot overcome what happened. (Archive of Antje Scherret) A civil servant is promised he will be appointed as the head of his agency within a year. He is preparing himself for this; however, he is suddenly confronted with the fact that a colleague, who he absolutely cannot stand, will get the post = hardly digestible, ugly situation > cell division in the deep-lying mucosa of the bladder in the active-phase, purulent bladder inflammation in the repair phase. (Archive B. Eybl) A civil servant is promised he will be appointed as the head of his agency within a year. He is preparing himself for this; however, he is suddenly confronted with the fact that a colleague, who he absolutely cannot stand, will get the post = hardly digestible, ugly situation > cell division in the deep-lying mucosa of the bladder in the active-phase, purulent bladder inflammation in the repair phase. (Archive B. Eybl) |
| Tissue | Bladder – trigon mucosa – brainstem – endoderm; usually the “bladder triangle“ (the region between the mouths of the ureters and the outflow of the urethra) is affected and also the regions under the superficial urothelium mucosa (submucosa). Approximately 10% of bladder tumors are of this type. |
| Conflict-active | Conflict–active Increase in function, growth of a cauliflower-like tumor of secretory quality or a flat-growing tumor of absorptive quality = endodermal bladder cancer. |
| Bio. function | Secretory type: “digestion“ of the outrage; absorptive type: absorption of urine analog to the kidney collecting tubules SBS“ absorption“ of the ugly situation. |
| Repair phase | Degradation of the tumor = purulent bladder infection, pus, blood in the urine, pain, night sweats. |
| Repair crisis | Chills, severe pain, blood in the urine. |
| Questions | Which ugly situation was I unable to tolerate? (Conflict, betrayal, disappointment, deceit in a partnership, at the workplace, between family members)? Why am I still preoccupied by this matter? What from my childhood reminds me of the issue? What has conditioned me additionally? Do my parents act in the same way? Which beliefs should I get rid of? (E.g., too many expectations)? Which new inner attitude would help? (E.g., total forgiveness, see the good in those involved). |
| Therapy | With inflammation: the conflict is resolved. Support the healing process. Colloidal silver internally. Tumor without inflammation: Identify the conflict, triggers and conditioning and resolve them in real life if necessary. MMS (see p. 68). Surgery, if the tumor is too large. For bladder remedies, see: p.292. |
1 See Dr. Hamer, Charts p. 29
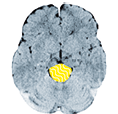
Irritable/overactive bladder, imperative urinary incontinence
Constant urge to urinate, frequent urination with only small amounts of urine, is called an overactive bladder.
| Conflict | A person‘s borders are not respected by others because they have not marked them clearly. One feels or puts themselves under pressure. One is unsure and easily influenced regarding one’s own decisions. |
|---|---|
| Examples |  A man must share an apartment with his son and his son’s family. He doesn’t like the situation and suffers greatly. Just to get to his own room, he has to walk through the others‘ living area. The man starts suffering from “irritable bladder,“ a conflict of not being able to mark his territory clearly. He wants to mark it, but cannot because he doesn’t want to upset the family. (Archive B. Eybl) A man must share an apartment with his son and his son’s family. He doesn’t like the situation and suffers greatly. Just to get to his own room, he has to walk through the others‘ living area. The man starts suffering from “irritable bladder,“ a conflict of not being able to mark his territory clearly. He wants to mark it, but cannot because he doesn’t want to upset the family. (Archive B. Eybl) A 64-year-old, divorced retiree has to get up seven or more times in the night and then urinates only small amounts of urine. The doctors tell him his prostate is fine. Conflict: following his failed marriage, the patient cannot bear to think about marrying for a second time. However, his girlfriend of many years wants to marry = territorial-marking conflict affecting the involuntary bladder musculature. Often, when she comes home from work in the evening, she starts with the same unpleasant topic = recurrence. The evenings and nights at home have become “triggers“ for the patient. Conflict activity in the evenings and nights; thus, he has massive sleep disturbances. During vacations, the problem is reduced. (Archive B. Eybl) A 64-year-old, divorced retiree has to get up seven or more times in the night and then urinates only small amounts of urine. The doctors tell him his prostate is fine. Conflict: following his failed marriage, the patient cannot bear to think about marrying for a second time. However, his girlfriend of many years wants to marry = territorial-marking conflict affecting the involuntary bladder musculature. Often, when she comes home from work in the evening, she starts with the same unpleasant topic = recurrence. The evenings and nights at home have become “triggers“ for the patient. Conflict activity in the evenings and nights; thus, he has massive sleep disturbances. During vacations, the problem is reduced. (Archive B. Eybl) An 8-year-old girl has to share her room with her sister. After a big fight over the toys, she wets the bed. = Territorial-boundary conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) An 8-year-old girl has to share her room with her sister. After a big fight over the toys, she wets the bed. = Territorial-boundary conflict. (Archive B. Eybl) |
| Conflict-active | Conflict–active Heightened tension (hypertonia) of the bladder muscle, muscle thickening (hypertrophy) = so-called irritable bladder. |
| Bio. function | Strengthening of the bladder muscle so that the urine can be eliminated in a stronger stream in order to better mark one‘s territory. |
| Repair phase | Normalization of tension; the muscle remains thickened. |
| Repair crisis | Tonic-clonic bladder cramps, immediate urge to empty the bladder, “imperative.“ |
| Note | The symptoms are much like those of a recurring inflammation of the bladder‘s mucous membrane. The two are difficult to tell apart – they are possibly connected. The conflict contents are similar as well. |
| Questions | Imperative during which situations? (Indication of the trigger). Why do I allow myself to be put under pressure? Which personality structure makes this possible? Do I want to have good relations with everyone at any price? How do I deal with authority? Do I feel weak in comparison? What conditioned me? (Childhood, pregnancy, parental style, ancestors)? Which new attitude do I want to cultivate? |
| Therapy | Identify the conflict and conditioning and resolve them, so that the tension in the bladder lets up. Guiding principles: “I make my decisions with confidence.“ “I won‘t let myself be put under pressure.“ With children, create visible and practical solutions. For bladder remedies, see: p.292. Pelvic floor training, pubococcygeus muscle training – practice voluntary tensing up and relaxing. |

Residual urine
| Conflict | Not being able to sufficiently hold back one‘s urine. |
|---|---|
| Examples | ➜ Occurs frequently after prostate surgeries. Eight years ago, a now 64-year-old patient was still not familiar with the 5 Biological Laws of Nature and agreed to prostate surgery. Since then, he is impotent and incontinent. When he carries something heavy, a few drops always spill into his pants = conflict of not being to hold back one‘s urine > strengthening of the inner sphincter muscle of the bladder. Years of conflict activity have made his urine stream weak, and he always has to press. (Archive B. Eybl) Eight years ago, a now 64-year-old patient was still not familiar with the 5 Biological Laws of Nature and agreed to prostate surgery. Since then, he is impotent and incontinent. When he carries something heavy, a few drops always spill into his pants = conflict of not being to hold back one‘s urine > strengthening of the inner sphincter muscle of the bladder. Years of conflict activity have made his urine stream weak, and he always has to press. (Archive B. Eybl) A patient, now 62-years-old, remembers his terrible experience as a three-year-old, as if it was yesterday: his very dominant mother goes shopping, leaving him at home alone. Before going out she threatens the boy: “You‘d better not wet your pants, while I‘m gone.“ As the child‘s urge to urinate becomes greater, he hops about, constantly losing urine and dreading the consequences > increased tension in the inner sphincter muscles. Since then he must always be alone to urinate and always has residual urine. (Archive B. Eybl) A patient, now 62-years-old, remembers his terrible experience as a three-year-old, as if it was yesterday: his very dominant mother goes shopping, leaving him at home alone. Before going out she threatens the boy: “You‘d better not wet your pants, while I‘m gone.“ As the child‘s urge to urinate becomes greater, he hops about, constantly losing urine and dreading the consequences > increased tension in the inner sphincter muscles. Since then he must always be alone to urinate and always has residual urine. (Archive B. Eybl) |
| Conflict-active | Conflict–active Increased muscle tension (hypertonia), problems when urinating, weak stream, residual urine because the inner sphincter muscle does not open completely. Usually a recurring–conflict. |
| Bio. function | Strengthening of the inner sphincter so that the urine can be withheld better. |
| Repair phase | Normalization of muscle tension; in the repair phase crisis, periods of incontinence and cramps. |
| Questions | First, determine if the symptoms come from the prostate. If no: residual urine since when? (OP, anesthesia, accident, embarrassing situation)? Substitution conflict? (Sympathy with others)? Which conditioning could play a role? (Parents, birth, pregnancy, early childhood)? Which thought(s) give relief? Which traditional belief do I want to throw overboard? |
| Therapy | Determine and resolve the conflict and conditioning in real life. Pelvic floor training, pubococcygeus muscle training – tensing up and relaxing exercises. For bladder remedies, see: p.292. |
Urine loss – stress incontinence
| Conflict | Wanting or not being able to retain the urine (special territory marking conflict). |
|---|---|
| Examples | ➜ An elderly woman contracts a bladder infection and cannot control her urge to urinate = self-esteem conflict: “Now I am probably incontinent.“ ➜ A man doesn‘t dare to put his mother-in-law in her place because he is afraid of causing a family argument > he wants to “draw the line“ but cannot for family reasons = self-esteem conflict. |
| Conflict-active | Degradation of cells or limited innervation of the external bladder sphincter > the urine cannot be fully retained voluntarily = “weak bladder,“ stress incontinence. Loss of a small amount of urine when lifting, coughing, sneezing, laughing, etc. Usually a recurring–conflict. |
| Repair phase | Restoration (sphincter-hyperplasia) > recovery of innervation, possibly residual urine. |
| Repair crisis | Loss of urine because the sphincter muscle opens in an uncoordinated manner > incontinence. |
| Bio. function | Strengthening of the external sphincter muscle so that the urine can be retained better. |
| Note | During old age, this can also occur without a conflict: diminishing physical and muscular tension can lead to a slackening of the sphincter apparatus. |
| Therapy | Identify the conflict, conditioning and resolve them in real life. Exercises for the pelvic floor and for breathing; buildup of body tension, regulate body weight. If necessary, bladder ligament or bladder lift surgery. For bladder remedies, see: p.292. |
Urinary incontinence (leaking)
Possible causes:
• Prostate OP: Injury to the bladder sphincter. Some stress incontinence (urine leakage when lifting, pushing) is normal during the first months, but unfortunately sometimes the problems persist.
• Accident/injury: Injury to the bladder sphincter nerves.
• Neurological disease: MS, Parkinson’s, and strokes are often accompanied by incontinence (see p. 289, 290).
• Muscle weakness: slackening of the sphincter musculature due to decreasing bodily tension and muscle tone with age. Mostly affected are women with weak connective tissue > stress incontinence (see also chapter: Connective Tissue p. 346, Uterine Prolapse p. 302).
• Urinary tract infection (UTI): SBS of the bladder mucosa – healing phase. Frequent/sudden urge to urinate. Sometimes, loss of urine from not reaching the toilet in time (see p. 286).
• Overactive bladder (OAB, “urge incontinence”): SBS of the smooth bladder musculature, usually a chronic conflict, see p. 289.
Therapy
According to the cause. Build up body tension (strength training, pelvic floor training, PC training) Keep body weight low. If necessary, potassium supplementation, magnesium chloride(MgCl2) foot baths, cannabis or hemp tea. If necessary, bladder tack (TVT) surgery or a pessary/other treatment options in the case of a prolapsed bladder.
See also remedies for the bladder p. .292.
Residual urine – other possible causes
• Prostate excretory ducts or prostate gland in healing or chronic persistent conflict: Swelling of the prostate excretory ducts is causing a backup in the bladder. This is probably the most common cause of residual urine in men. (See: p.317 and 315)
• Urethritis: Temporary residual urine for the duration of the inflammation: the urethral squamous epithelium swells up, resulting in obstruction and residual urine (see: p.286).
• Internal urethral sphincter (smooth muscle): Sphincter hyperplasia. Not being able to retain urine adequately. Not being allowed to urinate. Muscle tension increase (hypertonus) in active phase. > Weak stream, residual urine. Biological sense: strengthening of the sphincter muscle , so that the urine can be held better.
a The patient, now 62 years old, can still remember a terrible experience when he was three years old: His domineering mother left him alone at home because she had to go shopping. Before leaving, she threatened the boy, “Don’t you dare pee your pants!” When the boy can no longer hold back the urge, he bounces around the apartment, constantly losing urine, in a frightened panic about being punished = conflict, not being able to hold back the urine sufficiently. Since then he can only urinate alone and always has residual urine. (Archive B. Eybl).
• External urethral sphincter in persistent repair: high tension in the bladder sphincter during the repair phase > residual urine (see stress incontinence p. 290).
• Urethritis: rare. Conflict that one’s masculinity is restricted/territorial marking conflict in healing. Only temporary, residual urine for the duration of the inflammation. Swelling of urethral squamous epithelium, resulting in obstruction of outflow and residual urine (see cystitis p. 286).
• Chronic urethral stenosis: rare. Chronic conflict that one’s masculinity is restricted/territorial marking conflict, backlog or residual urine due to stenosis (p. 323).
Bladder stones,urinary stones
• “Primary urinary stones“ form in the bladder. Here, either SBS is possible (see: p.286 and 288).
• “Secondary urinary stones“ come from the kidneys and are triggered either by an SBS of the kidney collecting tubules or an SBS of the renal pelvis (see: p.277 and 282).
Therapy
Identify the conflict, trigger(s) and conditioning, so that no new stones appear.
Drink enough fluids, “soft“ water if possible and eat low-protein foods. If necessary, surgical removal of the stones.
• Teas: sage (also recommended by Hildegard), fennel, club moss, chamomile, horsetail, common daisy (Bellis perennis), speedwell, oak, etc.
• Kanne Bread Drink.
• For acute repair phases: drink plenty of fluids, especially beer.
• Massages for lower back, buttocks and legs.
• Foot reflex massage, acupoint massage.
• Keep the feet warm, take hot foot baths.
• Full hot baths, possibly with salt or tea added.
• MMS (see p. 68)..
• Antibiotics help with bladder and kidney pain. It makes sense for persistent repair.
• Pelvic floor exercises, pubococcygeus muscle training – promote a strong bladder and vigor; for general energy – this body region is the basis of the life-energy (root chakra).
• Best time for bladder treatments according to the organ clock: 4 pm.
All experience reports on the organ system „Bladder and Urethra“ from the International Report Archive:
| Author | Title and Overview | Keywords | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 2024/03/28  | |||||
 | 2023/01/21  | |||||
2021/06/17    An 11-year-old boy shared a room with his big brother and reacted in this context with a territorial marking conflict with bed-wetting as a consequence. By understanding the cause, a real solution was quickly and easily found here by finally giving the boy his own room. From now on, the bed-wetting disappeared. | ||||||
2017/12/21     Territory marking conflict on vacation when the cleaning lady entered the couple's room and bedroom in the morning without notice. Since then, daily reactivation of SBS with numbness of the bladder mucosa in the room - and resolution with hypersensitivity as soon as they left the room. | ||||||
2015/01/23     Severe bladder infection after acoustic borderline assault in dormitory. Two-phase very well comprehensible. |
